How to Fix and Diagnose File System Errors with CHKDSK.
If your computer is slow, it crashes or freezes when you try to access files or programs then you probably have errors on your hard drive. Fixing and diagnosing errors on your hard drive can protect you from the nasty situation of completely loosing your critical files, but it can also fix several Windows problems on your system.
Windows Check Disk tool (ChkDsk) can diagnose and correct file system errors that can occur after a power failure or after an interrupted installation of a Windows update or program. Keep in mind that you can use the check disk tool to determine problems on all hard drives or removable devices (e.g. USB memory stick) attached on your computer.
In a previous tutorial I had mentioned the methods to test and diagnose your hard drive (HDD) for hardware problems. In this article I 'll show you the way diagnose and repair file system errors by using the Windows "CHKDSK" command, plus the way to find out your disk's health status by reading the Check Disk's scanning results (log) after execution.
Part 1. How to diagnose, fix and repair file system errors using Check Disk tool.
Part 2. How to view Check Disk details log.
Part 1. How to diagnose, fix and repair file system errors (Windows 8, 7, Vista and XP).
Please Note: You can run Check Disk tool either from Windows GUI or from a command prompt. But, If you own a Windows 8 (or 8.1) computer, it is better to run the check disk tool from the Command prompt because in Windows 8 GUI there is not an available option to scan and repair bad sectors. (For that case I prefer to always run 'Chkdsk" in any OS using the command prompt method).
Method 1: Use Check disk tool in Windows GUI.
Method 2: Run Check Disk tool from Command Prompt
Method 1: How to run Check disk tool from Windows GUI.
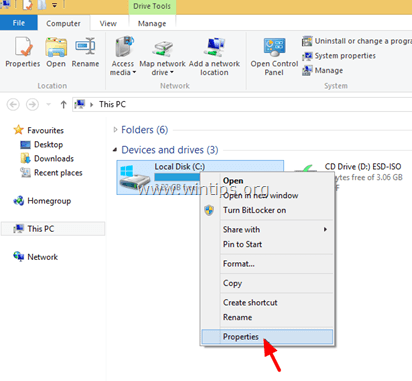
1. Open Windows Explorer (press Win + E keys).
2. Right-click on the disk that you want to diagnose and fix errors (e.g. your primary (root) disk "C:") and select Properties.
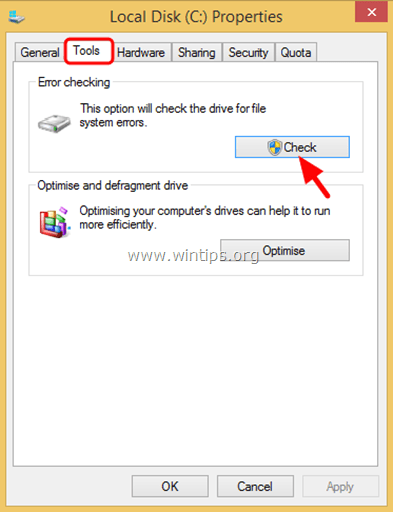
3. At Tools tab:
a. Press Check if you have Windows 8 or 8.1.
b. Press Check Now if you have Windows 7, Vista or XP.
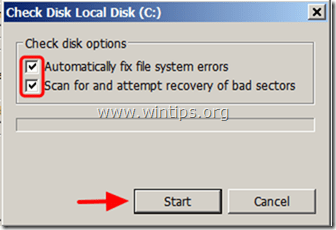
4a. Press Scan if you have Windows 8 or 8.1.
4b. Check the "Scan for and attempt recovery of bad sectors" checkbox and then press Start if you have Windows 7, Vista or XP (see screenshot).
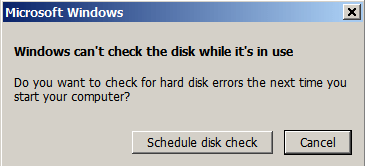
5a. If the disk is in use, then Windows asks you to schedule the scan the next time you start your computer. When you receive that message:
- Select Schedule disk check
- Click OK to exit disk properties.
- Close all programs and restart your computer.
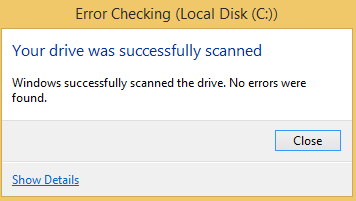
5b. If the disk is not in use, then the scan/repair process will start immediately and when it's completed, you should receive an information message (like the screenshot below).
6. Continue to Part 2 to view check disk's details (health status).
Method 2: How to run Check Disk from the Command Prompt.
Before continuing: Restart once your computer (to close all open programs) and disable any antivirus or/and backup programs that are currently running on your system.
1. Open an elevated command prompt. To do that:
In Windows 7 & Vista go to:
- Start > All Programs > Accessories
- Right-click at “Command prompt” item and choose “Run as administrator”.
In Windows 10, 8 & 8.1:
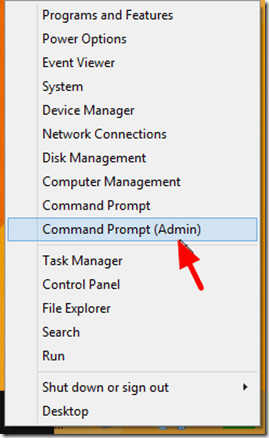
- Right-click at the screen's bottom-left corner and from the pop-up menu, choose “Command Prompt (Admin)”.
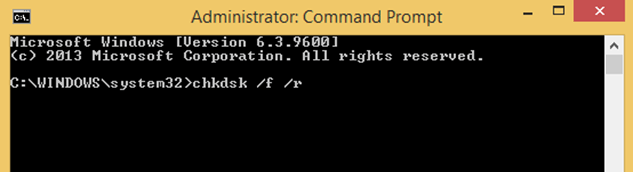
2. In the command prompt window, type the following command* and press enter:
- chkdsk %driveletter% /f /r
*Note: As %driveletter% type the drive letter of the disk (e.g. C:, E:, F:, etc.) that you want to check for errors as it appears in Windows Explorer.
For example:
- If you want to check and repair the root drive C: (where Windows are Installed On) then you have to type this command (there is no need to specify the drive letter for the root drive): chkdsk /f /r
- If you want to check and repair another drive (e.g. the drive "E:" ) then you have to type this command: chkdsk e: /f /r
3a. If you want to check the root drive ("C:"), you should receive a message-question that says "Chkdsk cannot run because the volume is in use by another process. Would you like to schedule this volume to be checked the next time the system restart? (Y/N)" (see screenshot below).
- Answer Yes to that question by pressing the Y key on your keyboard and press Enter.
- Restart your computer
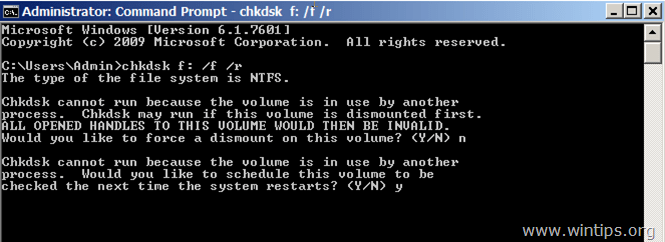
3b. If you want to check another drive than the root volume (drive) you should receive a message-question that says "Chkdsk cannot run because the volume is in use by another process. Chkdsk may run if this volume is dismounted first. ALL OPENED HANDLES TO THIS VOLUME WOULD THEN BE INVALID. Would you like to force a dismount on this volume? (Y/N)" (see screenshot below)
- Answer No to that question by pressing the N key on your keyboard and press Enter.
Then you should receive another message – question says that: "Chkdsk cannot run because the volume is in use by another process. Would you like to schedule this volume to be checked the next time the system restart? (Y/N)"
- Answer Yes to that question by pressing the Y key on your keyboard and press Enter.
- Restart your computer
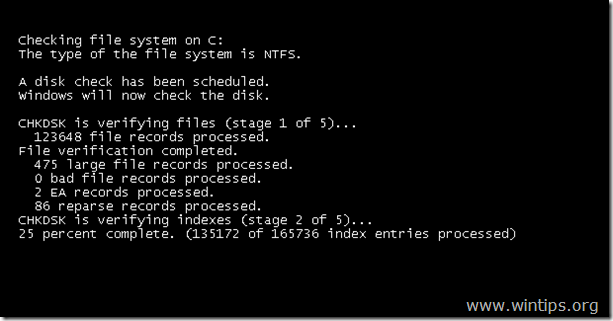
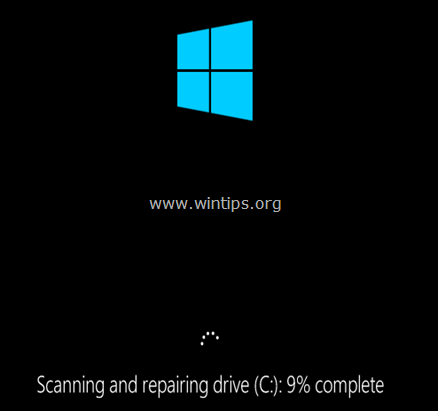
4. After the restart, the check disk operation should start. Wait until Windows check your disk for errors.
(screenshot: Windows 7, Vista, XP)
(screenshot: Windows 8)
5. When the check disk operation is completed Windows should enter normally to Windows. Follow the instructions below to read check disk's log file.
Part 2. How to view Check Disk's tool scanning results.
In order to view check disk's log (hard disk's health status) you have to navigate to Windows Event Viewer. To do that:
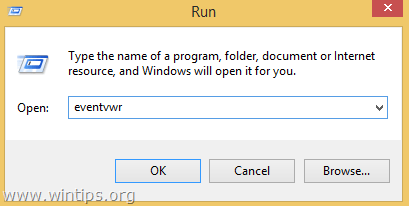
1. Press “Windows” ![]() + “R” keys to load the Run dialog box.
+ “R” keys to load the Run dialog box.
2. Type eventvwr and press Enter to open Event Viewer.
3. At the left pane, expand Event Viewer > Windows Logs > Application.
4. At the right pane, scroll down and double click to open the Wininit source. *
* Or go to main menu and select: Action > Find and in the Find What box, type: wininit
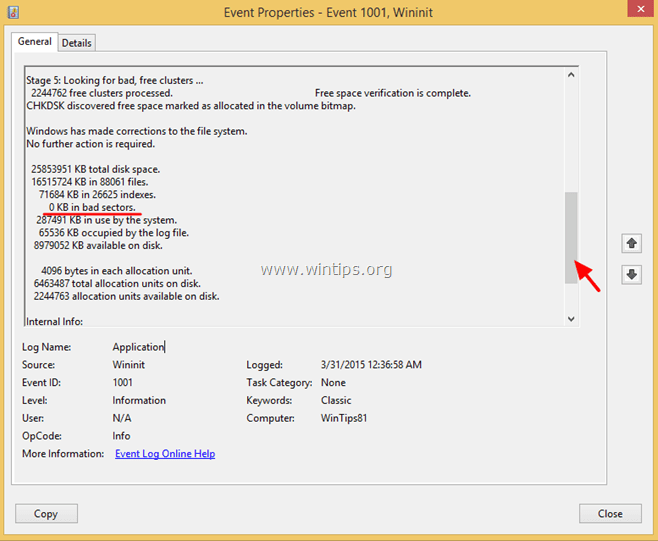
5. Here you can view a detailed log after a file system check that includes all actions and file system repairs that were made.
6. To find out your disk's health status, scroll down (using the scroll bar at the right) and read the KB value in bad sectors line:
- The value should be 0 (zero) in a healthy file system.
- If you see a positive value (e.g. "100KB in bad sectors") then the file system has problems, probably because your disk is defective (faulty) due to hardware problems and you have to replace it. (see suggestions below)
Suggestions:
- Always keep a backup copy of your important files to another storage media (e.g. USB memory stick, External Hard Drive, DVDROM, etc.) and keep this media Offline (Unplugged).
- Before proceeding to replace your hard drive, learn how to test and diagnose your disk for hardware errors.
That's it!
We're hiring
We're looking for part-time or full-time technical writers to join our team! It's about a remote position that qualified tech writers from anywhere in the world can apply. Click here for more details.
- FIX: Error 0x8007025d in Windows 10 Update. - April 22, 2024
- How to Disable Device Encryption in Windows 11/10. - April 17, 2024
- How to View Permissions on Shared Folders on Windows 10/11. - April 15, 2024





February 17, 2017 @ 12:07 pm
Thanks for this. Very informative article.